Differential scanning calorimeter BXT-DSC100L
Packing Size:
Gross Weight:
Packing Material:
Liquid/Battery/Motor:
HS Code:9027899090
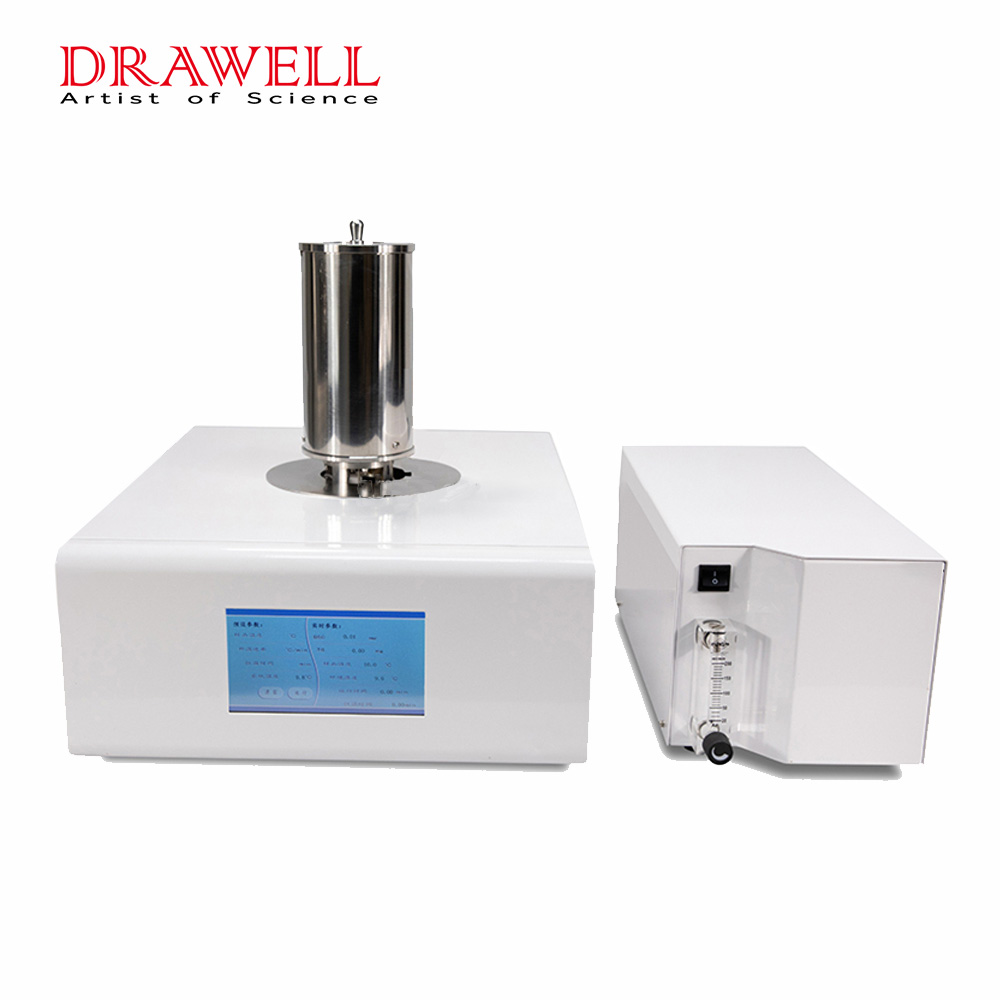
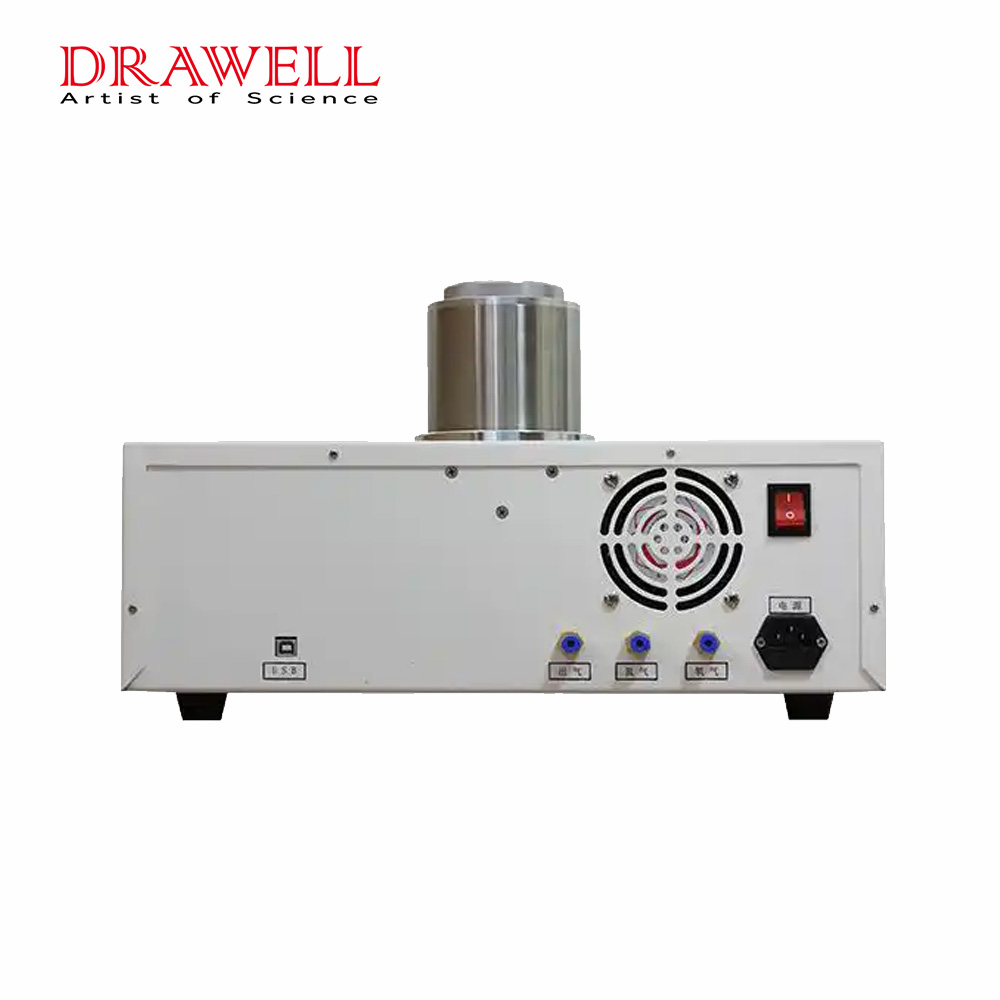


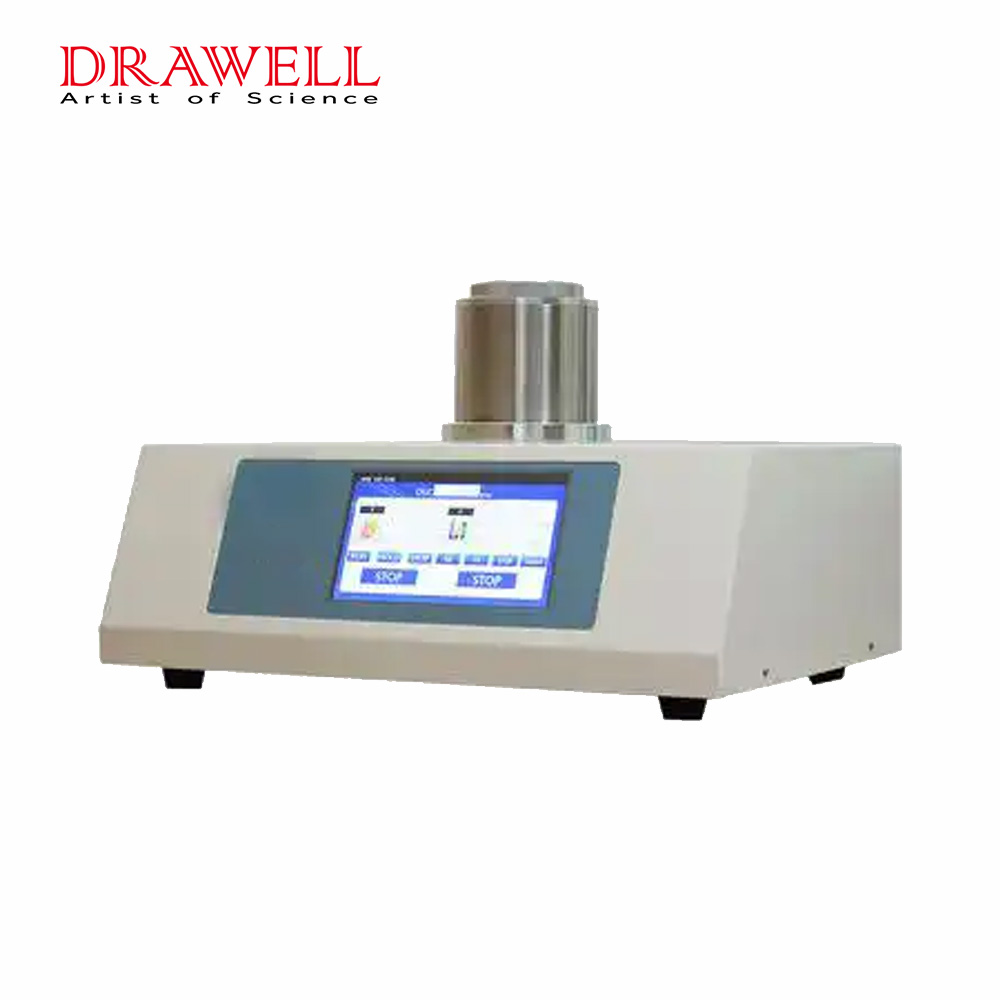








Introduction
Differential scanning calorimeter (heat flow DSC) is a classic thermal analysis method of thermal effects under controllable program temperature. It is used in the research and development, process optimization, quality control and failure analysis of various materials and chemistry fields. It has been widely used in various occasions. Using the DSC method, we can study the phase transition of inorganic materials, the melting of polymer materials, the crystallization process, the polymorphism of drugs, the solid/liquid ratio of foods such as oils and fats.
Features
1. The new fully enclosed metal furnace body design structure greatly improves the resolution and resolution and better baseline stability. To
2. Using professional alloy sensor, it is more resistant to corrosion and oxidation, and the sensor has high sensitivity.
3. Perfect two-way atmosphere control system, precise control of purge gas flow, automatic switching of software settings, and data directly recorded in the database.
4. Using Cortex-M3 core ARM controller, the calculation processing speed is faster, and the temperature control is more accurate.
5. Using USB two-way communication, the operation is more convenient and supports self-recovery connection function.
6. Using 7-inch 24bit color full-color LCD touch screen, real-time display of the status and data of the instrument.
7. The instrument is equipped with standard materials, and users can calibrate each temperature section by themselves to reduce the error of the instrument.
8. Intelligent software design, automatic drawing of the instrument in the whole process, the software can realize various data processing, such as the calculation of enthalpy, glass transition temperature, oxidation induction period, melting point and crystallization of substances, etc.
Applications
Measure physical and chemical changes related to heat, such as glass transition temperature, melting point, melting temperature, crystallization and crystallization heat, phase transition reaction heat, product thermal stability, solidification/crosslinking, oxidation induction period, etc. To